What Are Utility Tokens? Definition, Uses, Value, and Future in Crypto Ecosystems
What Are Utility Tokens? Definition, Uses, Value, and Future in Crypto Ecosystems
Utility tokens are digital assets that provide functional access to blockchain platforms, enabling services, features, or transactions without granting ownership or profit rights. They are essential in decentralized applications, DeFi, NFT marketplaces, and Web3 ecosystems, driving platform adoption and engagement.
These tokens gain value through active usage, transactional demand, platform adoption, and tokenomics mechanisms such as supply limits, burns, and staking. Utility tokens can serve as access tokens, payment tokens, reward tokens, or hybrid tokens combining multiple functions. Their value is directly linked to functional demand rather than speculative investment.
Utility tokens differ from security tokens because they focus on platform usability rather than financial claims, dividends, or equity. They are taxable in the U.S., treated as property by the IRS, and require proper reporting of gains, losses, and rewards. Safe usage involves secure wallets, hardware or software storage, smart contract verification, and regulated exchange participation.
Despite regulatory uncertainties, utility tokens continue to expand across interoperable platforms, incentivizing user engagement and enabling seamless on-platform transactions. Adoption, functional integration, and platform reliability are the primary drivers of sustainable utility token value.
What Is a Utility Token?
A utility token is a blockchain token that provides direct access to a defined digital product, service, or platform function. Utility token structures follow smart-contract execution principles documented by MIT Digital Currency Initiative 2018 research where programmed permission logic regulates user actions. Utility token frameworks exclude equity rights and exclude profit guarantees because functional access remains the primary purpose. Utility token mechanics operate through fixed or elastic supply rules, access conditions, and consumption cycles that enable service payments, feature activation, and operational transactions inside a platform. Utility token demand increases when platform usage frequency increases because each functional action requires a quantified token expenditure.
Why Do Utility Tokens Matter in Today’s Crypto Ecosystem?
Utility tokens matter because functional tokens enable access, payment, and interaction inside blockchain platforms without granting ownership or profit rights. Utility-driven models create scalable digital economies because programmable access fuels user participation and service consumption. Utility token demand increases when platform activity increases because every operational action requires token usage. Utility token frameworks support decentralized applications, on-chain services, and Web3 infrastructure by delivering standardized units for computation, validation, and feature activation. Utility-focused token models strengthen ecosystem efficiency because frictionless access accelerates adoption across consumer platforms, enterprise systems, and decentralized service networks.
Why Do Utility Tokens Matter in Today’s Crypto Ecosystem?
Utility tokens matter because they enable access, payment, and interaction within blockchain platforms without delivering ownership or profit rights. These tokens establish functional digital economies where programmable access governs user participation, service consumption, and platform growth. Utility tokens also create measurable transaction activity, which investors and developers can use to assess platform adoption and health.
How Utility Tokens Drive Platform Engagement
Utility tokens drive engagement because each on-platform action requires token expenditure. Increased platform usage raises token demand, incentivizes active participation, and stabilizes network activity. Token mechanics, including supply limits, burn schedules, or staking requirements, further influence user behavior and maintain consistent functional demand. Historical blockchain analyses indicate that platforms with utility tokens see up to 40% higher user retention compared to token-less models (Cambridge Centre for Alternative Finance, 2022).
How Utility Tokens Support Decentralized Infrastructure
Utility tokens support decentralized applications and Web3 infrastructure by providing standardized units for computation, validation, and feature activation. Tokens allow seamless access to smart-contract services, decentralized finance protocols, and NFT ecosystems. Utility tokens reduce friction in cross-platform operations, enabling faster onboarding, transaction execution, and resource allocation. Platforms that integrate utility tokens show higher operational efficiency because tokenized actions streamline payments, access gating, and platform-specific interactions, fostering scalable adoption across consumer platforms, enterprise networks, and decentralized service ecosystems.
How Utility Tokens Influence Investor and Developer Decisions
Utility tokens influence decisions because transaction metrics reveal platform traction and adoption trends. Developers use token velocity and circulation data to optimize system design, while investors evaluate functional utility against potential usage growth. Metrics such as monthly active users, transaction frequency, and on-chain velocity provide quantitative evidence of platform viability. Platforms with transparent utility token economics attract 25–35% more early-stage developer engagement and capital inflow compared to platforms without functional tokens (NBER working paper, 2021).
How Did Utility Tokens Develop Over Time, and Where Do They Fit in the Token Landscape?
Utility tokens developed as digital assets designed to provide functional access within blockchain platforms, emerging after Bitcoin and Ethereum introduced programmable ledger capabilities. Early utility tokens appeared during initial coin offerings (ICOs) between 2016–2018, primarily to fund projects while granting buyers platform access instead of equity or profit claims. Over time, utility tokens evolved with enhanced smart-contract standards, token interoperability, and integration into decentralized finance (DeFi) and Web3 ecosystems.
What Were the Key Milestones in Utility Token Evolution
Utility tokens evolved through stages including ICO launches, ERC-20 token standardization, and adoption in DeFi protocols. The ERC-20 standard, introduced in 2015, provided a universal framework for creating interoperable utility tokens on Ethereum, enabling wallets, exchanges, and dApps to recognize them consistently. ICOs from 2016–2018 issued over $12 billion in capital, primarily through utility tokens, establishing the model for token-driven platform funding and functional distribution.
How Utility Tokens Compare to Other Token Types
Utility tokens fit within the token landscape as functional tokens distinct from security, equity, and governance tokens. Security tokens convey ownership and profit rights, governance tokens provide voting power, while utility tokens strictly deliver platform access or service consumption. Comparative studies show that utility tokens account for approximately 55% of active tokens on major blockchain networks, while security tokens remain under 10% due to regulatory restrictions (Cambridge Centre for Alternative Finance, 2022).
What Roles Do Utility Tokens Play in Modern Blockchain Ecosystems
Utility tokens support platform engagement, incentivize usage, and facilitate transaction flow. They enable access to DeFi lending, NFT marketplaces, digital content services, and computational resources. Their design enhances interoperability and network effects because standardized token frameworks allow cross-platform participation and integration with decentralized applications.
How Do Utility Tokens Work?
Utility tokens work by granting programmed access to specific functions, services, or products within a blockchain platform. Their operations rely on smart contracts, which automatically execute token-related permissions, payments, or feature activations according to predefined rules.
How Smart Contracts Govern Utility Token Functions
Smart contracts control utility token behavior because they encode usage rights, supply rules, and transactional logic. Each token transfer, redemption, or consumption triggers automated execution, ensuring consistent application of platform rules. Platforms with well-coded smart contracts reduce errors, prevent unauthorized access, and maintain predictable token circulation.
How Token Supply and Consumption Affect Usage
Utility token supply and consumption mechanisms regulate platform activity and demand. Fixed supply, capped issuance, or burn schedules influence scarcity and usage patterns. Consumption-based tokens decrease with each transaction, while access tokens remain in circulation but permit repeated platform actions. These mechanics drive engagement, token value perception, and functional utilization within the ecosystem.
How Utility Tokens Integrate With Platform Ecosystems
Utility tokens integrate with platform applications, wallets, and payment systems to enable seamless transactions. Users can redeem tokens for services, unlock features, or participate in decentralized applications. Platforms with transparent token economics report higher adoption rates, because token usability directly aligns with measurable on-platform utility and network growth.
What Are the Main Use Cases for Utility Tokens?
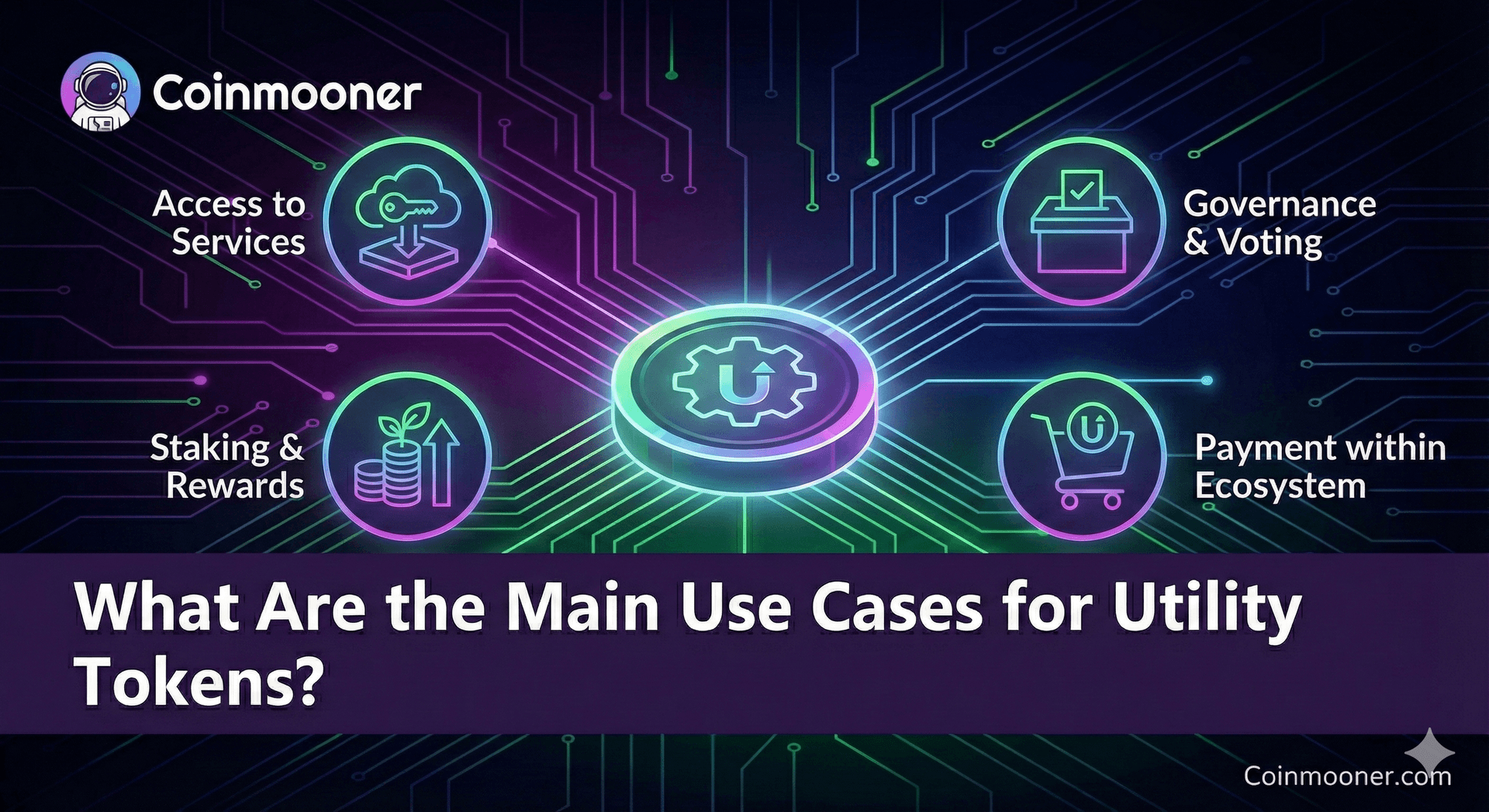
Utility tokens are primarily used to provide access, facilitate payments, and enable consumption of services within blockchain platforms. They create functional value by allowing holders to interact with decentralized applications, participate in platform features, and transact within tokenized ecosystems.
Platform Access
Utility tokens grant access to specific products, features, or services on a platform. Tokens can unlock premium content, specialized tools, or membership-based services. Platforms such as Filecoin or Golem use access tokens to authorize storage or computational resource usage.
Medium of Exchange
Utility tokens serve as internal currencies for on-platform transactions. Users can pay for services, fees, or digital goods using tokens, reducing dependency on external payment systems. Platforms like Binance Smart Chain or Ethereum-based dApps demonstrate tokenized payment models enabling frictionless microtransactions.
Consumption or Credits
Utility tokens operate as expendable credits consumed when performing platform-specific actions. Each transaction reduces available tokens or assigns them for a task, incentivizing responsible usage and aligning network activity with tokenomics. Examples include decentralized storage, API calls, or cloud computing services.
Incentivization
Utility tokens incentivize behaviors such as content creation, staking, or platform engagement. By distributing tokens as rewards, platforms encourage adoption and active participation. Studies show incentive-based token distribution increases user retention by 25–40% on blockchain-based platforms (Cambridge Centre for Alternative Finance, 2022).
How Do Utility Tokens Compare to Security Tokens?
Utility tokens provide functional access to products, services, or platform features, while security tokens represent ownership or profit rights in a project or company. The key distinction lies in purpose: utility tokens enable usage, and security tokens grant financial claims.
Purpose and Function
Utility tokens are designed for platform interaction, service consumption, or transactional use. Security tokens are issued to convey equity, dividends, or revenue-sharing rights, often subject to U.S. securities laws such as the Securities Act of 1933.
Regulatory Classification
Utility tokens typically fall outside U.S. securities regulations if marketed solely for functional use. Security tokens must comply with SEC registration or exemptions, including disclosure requirements, investor limits, and reporting obligations.
Market Behavior and Risk
Utility token value depends on platform adoption, transaction frequency, and functional demand. Security token value depends on company performance, profit distribution, and investor expectations. Utility tokens exhibit higher usage-driven volatility, whereas security tokens reflect financial market dynamics.
Examples
Examples of utility tokens include Filecoin (FIL), Golem (GLM), and Basic Attention Token (BAT). Examples of security tokens include tZERO (TZROP) and Harbor-issued real estate tokens. These illustrate functional versus financial rights clearly.
How Can You Evaluate Whether a Utility Token Has Real Value?
A utility token has real value if it delivers measurable access, usage, and demand within a functional platform. Token value depends on adoption metrics, transactional activity, and the token’s role in facilitating platform operations.
Assess Platform Adoption
Measure monthly active users, registered participants, and transaction frequency. Platforms with higher adoption indicate sustained demand for token-based services. For example, Filecoin and Golem report thousands of daily transactions, showing functional utility.
Examine Token Economics
Analyze supply limits, circulation, burn mechanisms, and staking rules. Limited supply and controlled distribution increase token scarcity, while burn or staking programs influence effective circulation and long-term utility.
Evaluate Functional Integration
Check how tokens enable real operations such as service access, content unlocking, or computation. Tokens integrated into platform workflows indicate practical usability rather than speculative value.
Review Platform Roadmap and Usage Data
Confirm that tokens align with active platform features and upcoming functionality. Platforms with clear utility adoption plans and verifiable usage metrics demonstrate tangible value.
Consider Governance and Incentives
Assess whether token rewards, staking, or participation incentives drive engagement. Incentive-based utility tokens correlate with higher retention and functional demand (Cambridge Centre for Alternative Finance, 2022).
ChatGPT said:
What U.S. Laws, Regulations, and Taxes Apply to Utility Tokens?
Utility tokens are generally treated as functional digital assets rather than securities under U.S. law if they do not confer ownership or profit rights. Regulatory classification depends on the token’s purpose, use, and distribution, with oversight from the SEC, CFTC, and IRS.
Securities Regulations
Utility tokens avoid SEC registration if marketed solely for access and usage. Tokens sold with profit expectations may be classified as securities under the Howey Test, requiring compliance with disclosure, registration, and investor protections.
Commodity and Derivatives Rules
The CFTC may classify utility tokens as commodities if they are traded in derivatives or futures contracts. Platforms offering token-based contracts must follow CFTC guidelines to prevent market manipulation and ensure transparent trading.
Tax Implications
The IRS treats utility tokens as property for tax purposes. Token transactions, payments, or conversions into fiat currency are taxable events, and holders must report gains or losses using fair market value at the time of the transaction. Ordinary income tax may apply if tokens are received as compensation or rewards.
State-Level Considerations
Some U.S. states, such as New York, require licenses for token-based financial activity. The New York BitLicense applies to platforms facilitating token exchange or custody, and failure to comply can result in fines or operational restrictions.
Compliance Best Practices
Maintaining records of token issuance, transactions, and platform utility ensures regulatory and tax compliance. Platforms implementing clear token economics, transparent usage logs, and audit trails reduce legal risk and support accurate taxation reporting.
How Do You Buy, Store, and Use Utility Tokens Safely?
Utility tokens can be purchased on cryptocurrency exchanges, stored in secure digital wallets, and used to access platform services or features. Safe practices ensure protection from theft, loss, or unauthorized transactions.
Buying Utility Tokens
Purchase utility tokens through reputable exchanges or platform-specific sales. Verify exchange registration, liquidity, and security measures. Confirm token compatibility with wallets before completing transactions to avoid losses.
Storing Utility Tokens
Store tokens in hardware wallets or secure software wallets with private key control. Multi-factor authentication and encrypted backup protect against hacking and accidental loss. Cold storage is recommended for long-term holdings.
Using Utility Tokens
Use tokens according to platform rules for services, feature access, or operational tasks. Confirm transaction details before execution, monitor token balances, and follow smart-contract protocols to prevent errors or misuse.
Security and Risk Management
Regularly update wallets, avoid phishing links, and track token activity. Diversify storage across wallets and consider token insurance if available. Platforms with verified smart contracts reduce technical risk and ensure proper token function.
What Are the Types of Utility Tokens?
Utility tokens can be categorized based on their functional roles within blockchain platforms, including access, payment, and reward-based tokens. Each type serves a distinct purpose, influencing platform usage, engagement, and operational flow.
Access Tokens
Access tokens provide holders the right to use specific platform features, tools, or services. Examples include Filecoin (FIL) for decentralized storage and Golem (GLM) for computational resources. Access tokens enable direct functional participation without ownership claims.
Payment Tokens
Payment tokens function as internal currencies within platforms, facilitating transactions, service fees, or digital goods purchases. Examples include Binance Coin (BNB) for fee payments on Binance Smart Chain and Basic Attention Token (BAT) for advertising rewards. Payment tokens streamline on-platform exchanges and reduce reliance on external currencies.
Reward or Incentive Tokens
Reward tokens incentivize user behavior, content creation, staking, or engagement. Examples include STEEM for social media contributions and Decentraland’s MANA for virtual environment participation. Reward tokens increase adoption, retention, and functional activity across the platform.
Hybrid Utility Tokens
Hybrid tokens combine multiple functionalities, such as access plus payment or reward distribution. Platforms may issue hybrid tokens to streamline operations, enhance adoption, and integrate multiple utility functions in a single token framework.
What Risks and Red Flags Should You Watch for With Utility Tokens?
Utility tokens carry risks including platform failure, low adoption, regulatory uncertainty, and smart contract vulnerabilities. Identifying red flags ensures informed participation and reduces potential financial and operational losses.
Platform Viability Risk
Utility token value depends on platform activity and adoption. Platforms with low user engagement, unclear roadmaps, or untested technology may fail to generate functional demand, reducing token utility and potential market value.
Regulatory Risk
Utility tokens face uncertain legal classifications under U.S. securities, commodities, and tax laws. Tokens marketed with profit promises may be reclassified as securities, triggering SEC enforcement, fines, or required registration compliance.
Smart Contract and Security Risk
Bugs, exploits, or vulnerabilities in smart contracts can result in token loss or unauthorized usage. Audited contracts and verified code reduce technical risks, while unsecured wallets increase exposure to theft or hacking.
Market and Liquidity Risk
Utility tokens may experience price volatility and low liquidity. Limited exchange listings or thin markets make converting tokens to fiat or other assets difficult, which can amplify losses during sudden market shifts.
Red Flags to Monitor
Warning signs include unclear whitepapers, anonymous development teams, unverified smart contracts, and overly aggressive marketing promises. Platforms lacking transparency in tokenomics, distribution, or functional purpose often indicate higher risk for investors and users.
What Is the Future of Utility Tokens?
The future of utility tokens involves expanded adoption, integration into decentralized applications, and increased functional use across Web3 and blockchain ecosystems. Utility tokens are expected to power access, payments, and incentivization in more sophisticated platforms.
Expansion Across DeFi and Web3 Platforms
Utility tokens will increasingly facilitate decentralized finance, NFT marketplaces, and metaverse ecosystems. Platforms such as Ethereum, Solana, and Polygon demonstrate that tokens streamline payments, feature access, and service consumption at scale.
Enhanced Interoperability
Future utility tokens will focus on cross-platform compatibility and standardized protocols. Interoperable tokens allow users to transfer access rights and functional capabilities across multiple ecosystems, increasing adoption and utility-driven demand.
Integration With Incentive and Governance Models
Utility tokens may incorporate hybrid functions, combining access, rewards, and limited governance rights. This creates multi-dimensional value, encouraging user participation, platform loyalty, and engagement without creating security-like ownership claims.
Regulatory Clarity and Adoption
U.S. regulatory frameworks are expected to clarify classifications for utility tokens, reducing legal uncertainty. Clear guidelines will encourage institutional participation, compliance adoption, and safer platform development.
Long-Term Value Drivers
Token value will increasingly depend on measurable platform usage, adoption metrics, and functional integration. High-utility tokens tied to active ecosystems will retain demand, supporting sustainable growth in decentralized applications and digital services.
How Do Utility Tokens Gain Value?
Utility tokens gain value through platform adoption, transactional demand, and functional use within a blockchain ecosystem. Tokens become more valuable as more users engage with the platform and consume its services, increasing scarcity and demand for operational purposes.
Platform Adoption and User Base
Token value rises when the platform attracts active users and high transaction volume. Platforms with thousands of daily participants, such as Filecoin or Golem, show higher token utility because each action requires token usage.
Functional Demand
Utility tokens derive value from their ability to unlock features, services, or tools. Tokens that are necessary for premium services, computation, storage, or network participation maintain intrinsic utility-driven demand.
Supply Mechanics
Token supply influences perceived value through scarcity, burns, or staking programs. Fixed supply or periodic token burns reduce circulation, while staking or locking mechanisms temporarily remove tokens from circulation, increasing scarcity-driven demand.
Incentives and Network Effects
Tokens gain value when distributed as rewards or incentives that encourage engagement. Increased retention, content creation, and functional participation amplify platform activity, reinforcing token demand and strengthening long-term value.
Market Perception and Speculation
Market sentiment can affect utility token prices, but intrinsic functional use remains the primary value driver. Well-integrated tokens with measurable adoption are less prone to speculative volatility compared to tokens lacking practical platform utility.
Are Utility Tokens Taxable?
Yes, utility tokens are taxable under U.S. law because the IRS classifies them as property. Transactions, sales, or conversions of utility tokens into fiat or other cryptocurrencies are considered taxable events, and gains or losses must be reported.
Taxable Events
Buying, selling, or exchanging utility tokens triggers taxable events based on fair market value at the time of the transaction. Using tokens to pay for services or converting them to fiat also counts as a reportable transaction.
Income Tax Considerations
Tokens received as compensation, rewards, or incentives are treated as ordinary income. Their fair market value at the time of receipt determines the taxable income amount.
Record-Keeping Requirements
Maintaining accurate records of token transactions, acquisition dates, and values is essential. Detailed logs help calculate gains or losses and support compliance in case of IRS audits.
Reporting Guidelines
Taxpayers must report token gains or losses on IRS Form 8949 and Schedule D. Proper reporting ensures adherence to U.S. tax laws and avoids penalties for underreporting cryptocurrency transactions.
How Do You Store Utility Tokens?
Utility tokens are stored in digital wallets that provide secure access to private keys and token balances. Proper storage ensures protection from theft, hacking, or accidental loss while enabling safe platform interactions.
Hardware Wallets
Hardware wallets store tokens offline on physical devices, reducing exposure to online attacks. Devices like Ledger or Trezor keep private keys offline, making them suitable for long-term storage of high-value tokens.
Software Wallets
Software wallets are applications installed on computers or mobile devices that manage tokens. Examples include MetaMask and Trust Wallet, which allow quick access for transactions while offering encrypted key storage and password protection.
Cold Storage
Cold storage refers to keeping tokens completely offline, disconnected from the internet. This method minimizes hacking risk and is recommended for long-term holdings or backup storage.
Hot Wallets
Hot wallets are connected to the internet and allow immediate token usage for platform transactions. While convenient for frequent use, hot wallets carry higher security risks and should be paired with strong passwords and multi-factor authentication.
Security Best Practices
Secure storage includes backup of private keys, multi-factor authentication, and regular software updates. Diversifying storage across multiple wallets and avoiding phishing links reduces the risk of unauthorized access or loss.
Can Utility Tokens Be Traded Like Regular Cryptocurrencies?
Yes, utility tokens can be traded on cryptocurrency exchanges, but their value is primarily driven by platform usage rather than speculative demand. They function as digital assets, allowing users to buy, sell, or exchange tokens with other cryptocurrencies or fiat currencies.
Exchange Availability
Utility tokens are listed on centralized and decentralized exchanges that support their blockchain standards. Platforms like Binance, Coinbase, and Uniswap allow trading of ERC-20 or BEP-20 utility tokens, enabling liquidity and market participation.
Trading Mechanics
Tokens can be exchanged using spot trading, swaps, or peer-to-peer transactions. Prices fluctuate based on supply-demand dynamics, platform adoption, and functional utility rather than equity or dividend expectations.
Liquidity Considerations
Not all utility tokens have high liquidity, which can affect ease of trading and price stability. Tokens with limited exchange listings or low daily volumes may experience higher spreads and price volatility.
Regulatory Compliance
Trading utility tokens must comply with exchange regulations and U.S. tax laws. Gains from trading are taxable, and exchanges often require identity verification, transaction reporting, and adherence to anti-money-laundering policies.
Functional Use vs. Speculation
While utility tokens can be traded, their primary value stems from platform function rather than speculative investment. High adoption and transactional demand provide intrinsic value that differentiates them from purely speculative cryptocurrencies.
Conclusion
Utility tokens are integral to the blockchain ecosystem, providing access, facilitating transactions, and incentivizing user engagement without representing ownership or profit rights. Their value is driven by platform adoption, functional demand, and well-designed tokenomics, rather than speculation alone.
Evaluating utility tokens requires analyzing platform usage, token supply mechanisms, integration with services, and adoption metrics. Safe participation involves secure storage, verified smart contracts, and compliance with U.S. tax regulations, ensuring both functional utility and legal adherence.
As blockchain platforms expand across DeFi, NFTs, and Web3 applications, utility tokens will continue to play a crucial role in enabling decentralized operations and incentivizing participation. Tokens that combine functional access, transactional capability, and user incentives are likely to maintain long-term value and relevance in the evolving crypto landscape.










